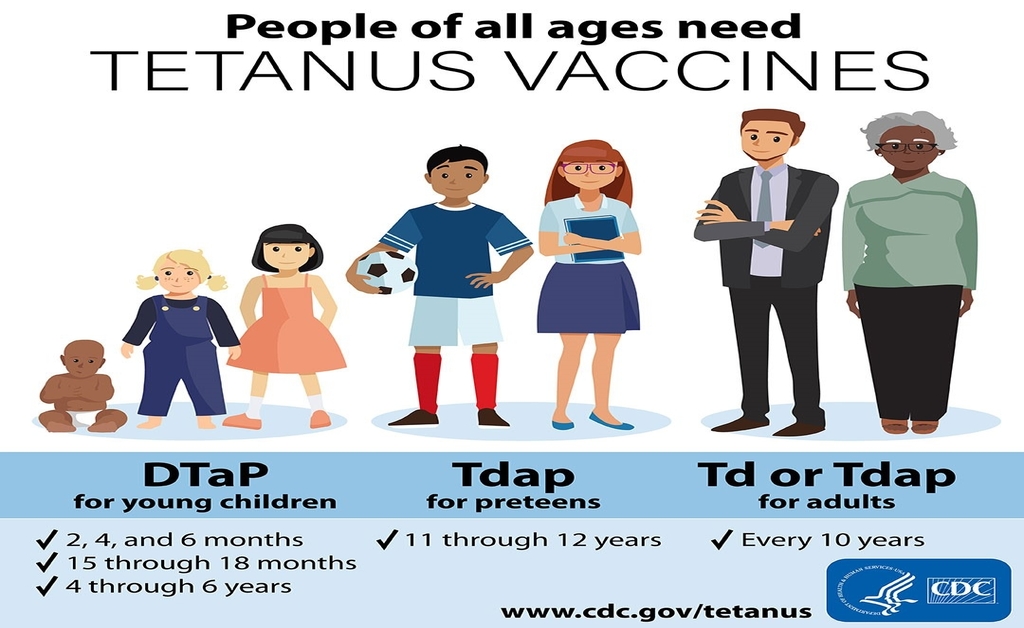
What are the ACIP recommendations for Adult Vaccination
August 20, 2020
0 Comments
Explore More
Diabetes Mellitus – Types, Symptoms, Treatment & Diet Plan
August 2, 2020
0 Comments
What is Diabetes Mellitus? Diabetes Mellitus is a disease group that affects how your body uses glucose. It can affect various organs of the body like the kidneys, feet, eyes
Endomedcare Joining Hands with HealisHealth
February 4, 2022
0 Comments
Endomedcare joining hands with Healis health
What Are The Causes, Symptoms & Treatment of Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
August 24, 2020
0 Comments
What causes Herpes Zoster (shingles)? Shingles is caused by varicella zoster which is the same virus that causes chicken pox. Chicken pox virus stays latent in the body after recovery.